3 月 . 04, 2025 10:08 Back to list
Common Nail
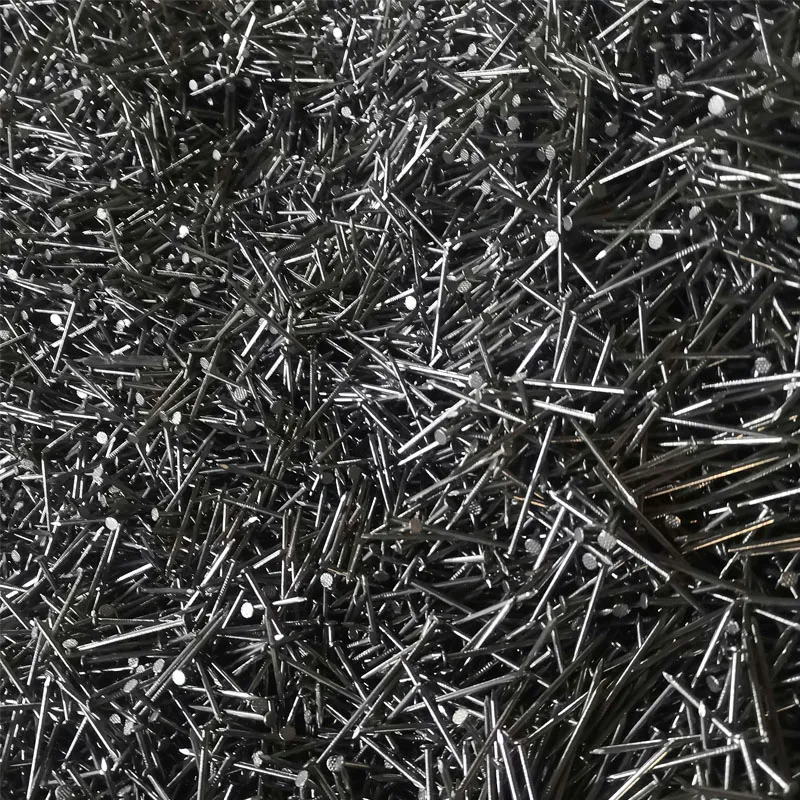
When evaluating the construction industry, one seemingly simple component plays an integral role—the 8 penny common nail. Behind its unassuming exterior lies a world of functionality, expertise, and trust, critical for both amateurs and seasoned professionals. Understanding the nuances of this fundamental product demands a deep dive into its application, benefits, and the expertise surrounding its use.
Authoritativeness emerges in the form of endorsements by industry associations and adherence to regional building codes. For professionals vested in sustainable building practices, these nails are often treated to resist rust and corrosion, extending their lifespan significantly. Such treatments are critical, especially in regions with high humidity or variable weather conditions, establishing the reliability of these nails as a worthy investment. The trustworthiness of the 8 penny common nail is further emphasized by its widespread adoption in myriad applications. From installing household baseboards to securing structural elements in commercial projects, these nails underpin efforts across a broad spectrum of tasks. This widespread application across varied environments underscores a collective trust within the building community, built upon decades of tried and tested functionality. Ultimately, the 8 penny common nail represents more than a simple fastener. It embodies a synergy of expertise, efficiency, and reliability. Builders and carpenters worldwide continue to endorse their worth, derived from years of consistent performance. For those in construction, understanding the subtle intricacies of these nails is crucial, allowing for projects that are both structurally sound and executed with precision. In summary, through experience and professional insight, the 8 penny common nail continues to be an emblem of reliability and a cornerstone of construction practices. Its historical roots, standardized measures, and adaptation to modern building codes cement its place as a trusted ally in both the amateur and professional builder's toolkit.
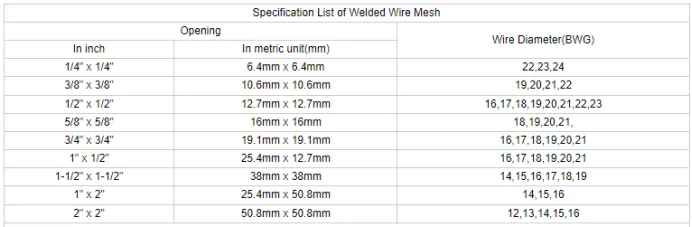
Authoritativeness emerges in the form of endorsements by industry associations and adherence to regional building codes. For professionals vested in sustainable building practices, these nails are often treated to resist rust and corrosion, extending their lifespan significantly. Such treatments are critical, especially in regions with high humidity or variable weather conditions, establishing the reliability of these nails as a worthy investment. The trustworthiness of the 8 penny common nail is further emphasized by its widespread adoption in myriad applications. From installing household baseboards to securing structural elements in commercial projects, these nails underpin efforts across a broad spectrum of tasks. This widespread application across varied environments underscores a collective trust within the building community, built upon decades of tried and tested functionality. Ultimately, the 8 penny common nail represents more than a simple fastener. It embodies a synergy of expertise, efficiency, and reliability. Builders and carpenters worldwide continue to endorse their worth, derived from years of consistent performance. For those in construction, understanding the subtle intricacies of these nails is crucial, allowing for projects that are both structurally sound and executed with precision. In summary, through experience and professional insight, the 8 penny common nail continues to be an emblem of reliability and a cornerstone of construction practices. Its historical roots, standardized measures, and adaptation to modern building codes cement its place as a trusted ally in both the amateur and professional builder's toolkit.
Next:
Latest news
-
Secure Your Roof with Quality Roofing Nails
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Secure Your Property with Quality Field Fencing
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Enhance Your Space with Quality Mesh Fencing
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Discover the Versatility of Iron Wire for Your Projects
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Discover the Versatility of Common Nails for Your Projects
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Discover Quality Hydraulic Fittings for Your Applications
NewsNov.04,2024









